The Effects of Digitalization in 2022 on the World Market

The spread of globalization has been significantly aided by developments in technology. In point of fact, the progression of technology has been one of the primary forces propelling globalization. Breakthroughs in technology make it necessary for businesses to expand into international markets since they increase the economies of scale and the minimum size of the target market that are required for the business to become profitable.
Because to technological improvements, the cost of traveling across countries and communicating with others has decreased, making it easier to source raw materials and other inputs from around the world. Technology that can be protected by a patent fosters globalization by allowing the company that owns the invention to enter overseas markets with little to no competition. The concepts of virtual and digital are simple to grasp.
The proliferation of information technology has contributed to the establishment of a worldwide community known as the “global village.” For instance, the advent of the World Wide Web has made it possible to conduct business transactions regardless of the time or location of the parties involved. Transactions between purchasers and vendors can now take place at any time of day or night and in any region of the world. Alterations in technology have an impact on investments as well. Following are various trends of Digital marketing:
- 5G Everywhere
- Semi-Conductors Eat the World
- Post-Pandemic Work Mega Shift
- Zero Trust Security
- Data Fabric
- Generative AI
5G Everywhere:
On the basis of exploration, it was stated last year that 5G would hit the mainstream in 2021, and its stands by that prediction. While sub-6GHz 5G projects have continued on schedule around the world, more advanced millimeter wave 5G deployments hold considerable growth potential.

Some early 5G deployments have carriers prioritizing low band 5G frequencies, which are almost twice as fast as LTE but often seem only marginally faster than LTE networks, leaving some analysts and consumers feeling dissatisfied with the spectacular 5G speeds we had been promised.
Semi-Conductors Eat the World:
In the year 2020, cloud, SaaS, collaboration, smartphones, and pretty much any technology that facilitated commerce, communication, and productivity experienced explosive expansion because of the epidemic. As a result of this pattern, 2021 has become the year of chip scarcity.

Vehicle and telecommunications manufacturing have also experienced significant setbacks as a result of this shortage. All four major chipmakers—Intel, Global Foundries, Samsung, and TSMC—have recently announced plans to invest billions in new fabrication factories in various locations worldwide to speed up production. But the chip industry is spending heavily to prevent future incidents.
Even while we won’t see the results of those investments until late 2020 or 2023 at the earliest, it’s important to recognize how massive they are and how crucial they will be to the growth of our infrastructure over the course of many years to come.
Post-Pandemic Work Mega Shift:
It was anticipated last year that remote work would persist even after the pandemic ended, and that is precisely what is happening. This summer, you may have noticed that several well-known businesses across various sectors have begun advertising flexible employment options.
However, there are difficulties inherent with such setups. With some personnel in the office and some still working remotely, businesses will require tools that make remote teamwork as easy as in-office meetings. Apparently, just 8% of meeting spaces worldwide have the technology necessary to support video conferencing. That’s the good news. Companies that rely on partnerships have taken notice.
Zero Trust Security:
The risk of cyberattacks has increased as a result of the widespread adoption of the remote-first culture by many enterprises. Therefore, it is very necessary to implement zero-trust security in order to demonstrate resilience.
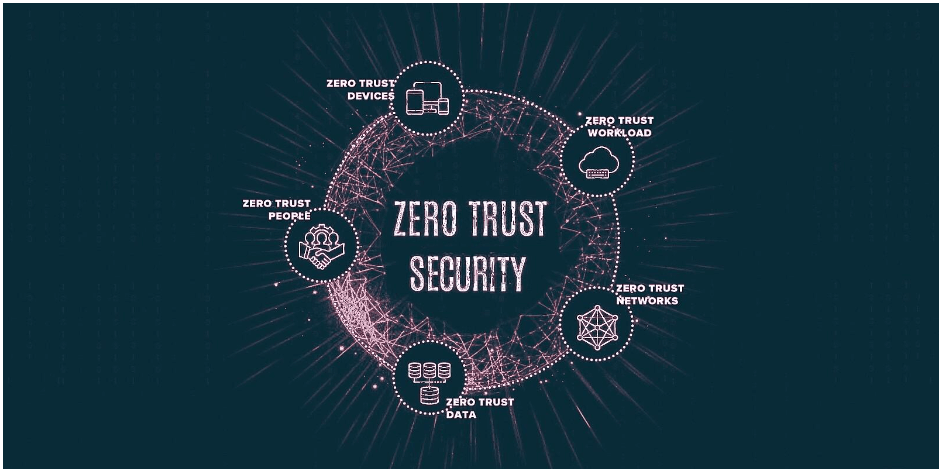
Migration to a cloud-based, zero-trust security architecture is already in many organizations’ planning and implementation stages. Establishing confidence, authority, and a positive brand reputation will be facilitated, as well as the beginning of secure B2B communication by the newly developed security solution.
Applications, data, identities, endpoints, networks, and even infrastructure can be better protected with the assistance of zero-trust security. The following are the three key tenets of the zero-trust security model: authenticated access, least privilege model, and inspect all Log Activities.
Data Fabric:
Gartner makes use of a compelling analogy to describe what data fabric is. Take into consideration an automobile that can drive itself as well as two scenarios that are connected. While the automatic features are not being utilized, the driver will physically operate the vehicle.
Second, when the driver loses concentration, the automatic features become active and make necessary adjustments to the route whenever they are needed. This is analogous to the operation of the data fabric. The data fabrics are helpful in making ideas that increase the productivity of the data teams.
After the data specialists have determined that the automated course corrections are adequate, control of the lever can be transferred totally to the data fabrics. This allows the data teams to concentrate on the most important aspects of their work while the data fabrics handle the mundane duties.
Generative AI:
Generative AI is a subfield of artificial intelligence that creates new content analogous to that already exists, such as pictures, texts, audio, and video, by utilizing previously created information. The most well-known application of generative AI is found in “Face” apps.
These apps need the user to upload a photo of themselves as an input, and then they display the user’s simulated appearance at various ages. In order to implement Generative AI, we can use one of three methods. A generational adversarial network (GAN) contains two different types of neural networks: a generating network and a discriminator network.
Final Words:
Every year, new exciting trends in digital transformation emerge, each of which has the potential to drive the growth of businesses. An organization’s use of digital technology will, in turn, spark disruption and drive profits. This is what is meant by the term “digital transformation.”
This blog post highlighted the top six digital transformation themes for the year 2022, which are as follows: 5G Everywhere; semi-conductors; post-pandemic work mega shift; zero-trust security; data fabric; and generative artificial intelligence.






