Penetration test (pen test)

What is a penetration test?
A penetration test, also called a pen test or ethical hacking , is a cybersecurity technique that organizations use to identify, test, and highlight vulnerabilities in their security posture. These penetration tests are often carried out by ethical hackers. These internal employees or third parties mimic an attacker’s strategies and actions to assess the hacking of an organization’s computer systems, network, or web applications. Organizations can also use penetration tests to prove their adherence to compliance regulations.
Ethical hackers are information technology (IT) experts who use hacking methods to help companies identify potential entry points to their infrastructure. By using different methodologies, tools, and approaches, companies can perform simulated cyberattacks to test the strengths and weaknesses of their existing security systems. Penetration , in this case, refers to the degree to which a hypothetical threat actor, or hacker, can penetrate an organization’s cybersecurity measures and protocols.
There are three main penetration testing strategies, each of which provides penetration testers with a certain level of information they need to carry out their attack. For example, white box testing provides the tester with all the details about an organization’s system or target network; black box testing does not provide the tester with any knowledge of the system; and the gray box penetration test provides the tester with partial knowledge of the system.
Penetration tests are considered a proactive cybersecurity measure because they involve constant, self-initiated improvements based on the reports generated by the test. This differs from non-proactive approaches, which lack foresight to improve weaknesses as they arise. A non-proactive approach to cybersecurity, for example, would involve a company updating its firewall after a data breach occurs. The goal of proactive measures, such as penetration testing, is to minimize the number of retroactive updates and maximize the security of an organization.
What is the difference between penetration testing and vulnerability assessment?
Penetration tests are not the same as vulnerability assessments, which provide a prioritized list of security weaknesses and how to fix them, but they are often done together. Penetration tests are often done with a particular goal in mind. These goals generally fall under one of the following three objectives:
- identify hackable systems
- try to hack a specific system
- carry out a data breach
Each goal focuses on specific outcomes that IT leaders are trying to avoid. For example, if the goal of a penetration test is to see how easily a hacker could breach the company’s database, ethical hackers would be instructed to try to carry out a data breach. The results of a penetration test will not only communicate the strength of an organization’s current cybersecurity protocols, but also present the available hacking methods that can be used to penetrate the organization’s systems.
Why are penetration tests important?
The rate of distributed denial of service, phishing, and ransomware attacks is increasing dramatically, putting all Internet-based businesses at risk. Considering how dependent companies are on technology, the consequences of a successful cyber attack have never been greater. A ransomware attack, for example, could prevent a company from accessing the data, devices, networks, and servers it depends on to conduct business. Such an attack could result in millions of dollars in lost revenue. Penetration testing uses the hacker’s perspective to identify and mitigate cyber security risks before they are exploited. This helps IT leaders implement informed security updates that minimize the chance of successful attacks.
Technological innovation is one of the biggest challenges facing cybersecurity, if not the biggest. As technology continues to evolve, so do the methods cybercriminals use. For companies to successfully protect themselves and their assets from these attacks, they must be able to update their security measures at the same rate. The caveat, however, is that it is often difficult to know what methods are being used and how they might be used in an attack. But, by using qualified ethical hackers, organizations can quickly and effectively identify, update, and replace the parts of their system that are particularly susceptible to modern hacking techniques.
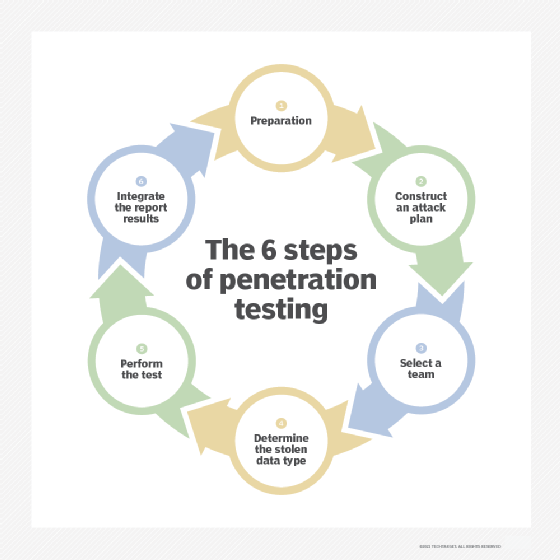
How to Penetrate Test
Penetration testing is unique from other cybersecurity assessment methods in that it can be tailored to any industry or organization. Depending on an organization’s infrastructure and operations, it may want to use a certain set of hacking techniques or tools. These techniques and their methodologies may also vary depending on your IT staff and your company’s standards. Using the following customizable six-step process, the penetration test creates a set of results that can help organizations proactively update their security protocols:
- Get ready. Depending on the needs of the organization, this step can be a simple or elaborate procedure. If the organization has not decided which vulnerabilities it wants to assess, a significant amount of time and resources must be spent combing the system for possible entry points. In-depth processes like this are generally only necessary for companies that have not yet done a full audit of their systems. However, once a vulnerability assessment has been performed, this step becomes much easier.
- Make a plan of attack. Before hiring ethical attackers, an IT department designs a cyberattack, or list of cyberattacks, that their team must use to perform the penetration test. During this step, it is also important to define what level of system access the pen tester has.
- Select a team. The success of a penetration test depends on the quality of the testers. This step is often used to designate the most suitable ethical hackers to perform the test. Decisions like these can be made based on employee specialties. If a business wants to test its security in the cloud, a cloud expert may be the best person to properly assess its cybersecurity. Companies also often hire expert consultants and certified cybersecurity experts to conduct penetration tests.
- Determine the type of stolen data. What is the team of ethical hackers stealing? The type of data chosen in this step can have a profound impact on the tools, strategies, and techniques used to acquire it.
- Take the test. This is one of the most nuanced and complicated parts of the testing process, as there are many automated software programs and techniques that testers can use, including Kali Linux, Nmap, Metasploit, and Wireshark.
- Integrate report results. Reporting is the most important step in the process. The results must be detailed so that the organization can incorporate the findings.






